Dentures
What Kinds of Dentures Are There?
 Complete & Partial
Complete & Partial
A denture is a removable dental appliance replacement for missing teeth and surrounding tissue. They are made to closely resemble your natural teeth and may even enhance your smile.
There are two types – complete and partial dentures. Complete dentures are used when all of the teeth are missing, while partial dentures are used when some natural teeth remain. A partial denture not only fills in the spaces created by missing teeth, it prevents other teeth from shifting.
A complete denture may be either “conventional” or “immediate”. A conventional type is made after the teeth have been removed and the gum tissue has healed, usually taking 4 to 6 weeks. During this time the patient will go without teeth. Immediate dentures are made in advance and immediately placed after the teeth are removed, thus preventing the patient from having to be without teeth during the healing process. Once the tissues shrink and heal, adjustments will have to be made.
They are very durable appliances and will last many years, but may have to be remade, repaired, or readjusted due to normal wear.
Reasons for Dentures:
- Complete Denture – Loss of all teeth in an arch
- Enhancing smile and facial tissues
- Partial Denture – Loss of several teeth in an arch
- Improving chewing, speech, and digestion
What does getting dentures involve?
The process requires several appointments, usually over several weeks. Highly accurate impressions (moulds) and measurements are taken and used to create your custom denture. Several “try-in” appointments may be necessary to ensure proper shape, colour, and fit. At the final appointment, the dentist will precisely adjust and place the completed denture, ensuring a natural and comfortable fit.
It is normal to experience increased saliva flow, some soreness, and possible speech and chewing difficulty, however this will subside as your muscles and tissues get used to the new dentures.
You will be given care instructions for your new dentures. Proper cleaning of your new dental appliance, good oral hygiene, and regular dental visits will aid in the life of your new dentures.
Implanted Supported Dentures
An implant-supported denture is a type of over-denture that is supported by and attached to implants. A regular denture rests on the gums, and is not supported by implants.
An implant-supported denture is used when a person does not have any teeth in the jaw, but has enough bone in the jaw to support implants. An implant-supported denture has special attachments that snap onto attachments on the implants.
There are two types of implant-supported dentures: ball-retained and bar-retained. In both cases, the denture will be made of an acrylic base that will look like gums. Porcelain or acrylic teeth that look like natural teeth are attached to the base. Both types of dentures need at least two implants for support.
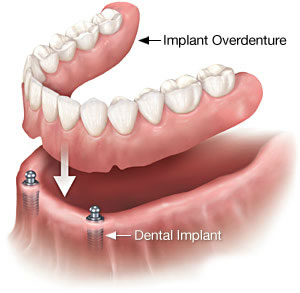
Ball-Retained Dentures (stud-attachment dentures):
Each implant in the jawbone holds a metal attachment that fits into another attachment on the denture. In most cases, the attachments on the implants are ball-shaped (“male” attachments), and they fit into sockets (“female” attachments) on the denture.
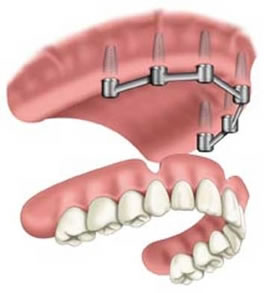
Bar-Retained Dentures:
A thin metal bar that follows the curve of your jaw is attached to two to five implants that have been placed in your jawbone. Clips or other types of attachments are fitted to the bar, the denture or both. The denture fits over the bar and is securely clipped into place by the attachments.
Request a Consultation
Please fill out this form to request your consultation. A member of our team will be in touch with you about your appointment as soon as possible.
Family Dental Services in Guelph
We pride ourselves on our high standard of patient care. Being a preventative practice, we are interested in your long term oral health. We offer a wide range of treatment options utilizing the latest technology. When you join the practice you join our family. Your needs are addressed with precision, compassion and understanding.
Contact Us
100 Edinburgh Rd S.
Guelph, ON, N1H 5P4
Phone: (519) 824 – 5678
Email: info@jaindentalcare.com
Clinic Hours
Monday: 8:00AM – 4:30PM
Tuesday: 8:00AM – 8:00PM
Wednesday: 8:00AM – 4:30PM
Thursday: 8:00AM – 8:00PM
Friday: 8:00AM – 4:00PM
